pprof #
pprof 是性能调试工具,可以生成类似火焰图、堆栈图,内存分析图等。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math/rand"
"net/http"
"time"
_ "net/http/pprof"
)
// 吃内存
type Eater struct {
Name string
Buffer [][]int
}
var e Eater
func main() {
e = Eater{Name: "eater"}
http.HandleFunc("/go", goHandler)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
// 如果不使用默认的 mux(http.DefaultServeMux),可以使用如下方式集成 pprof
// mux := http.NewServeMux()
// mux.HandleFunc("/go", goHandler)
// mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/", pprof.Index)
// mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/cmdline", pprof.Cmdline)
// mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/profile", pprof.Profile)
// mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/symbol", pprof.Symbol)
// mux.HandleFunc("/debug/pprof/trace", pprof.Trace)
// http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
fmt.Println(e.Name)
}
// 模拟创建 goroutine,内存没有及时回收
func goHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
go func() {
time.Sleep(time.Hour)
}()
e.EatMem()
}
w.Write([]byte("ok"))
}
func (e *Eater) EatMem() {
e.Buffer = append(e.Buffer, generateWithCap(1024*1024))
}
func generateWithCap(n int) []int {
rand.Seed(time.Now().UnixNano())
nums := make([]int, 0, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
nums = append(nums, rand.Int())
}
return nums
}
运行:
go run main.go
访问 http://localhost:8080/go 模拟业务。
访问 http://localhost:8080/debug/pprof/ 分析程序性能。
图形方式分析:
# 查看cpu
go tool pprof -http=:6060 http://127.0.0.1:8080/debug/pprof/profile
# 查看heap
go tool pprof -http=:6060 http://127.0.0.1:8080/debug/pprof/heap
# 查看goroutine
go tool pprof -http=:6060 http://127.0.0.1:8080/debug/pprof/goroutine
需要提前安装工具
Graphviz
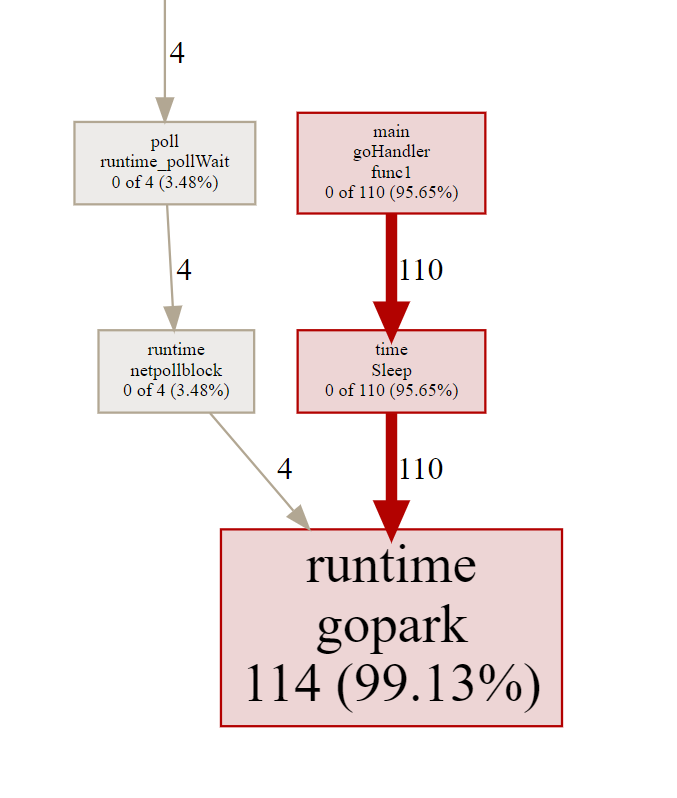
内存使用:
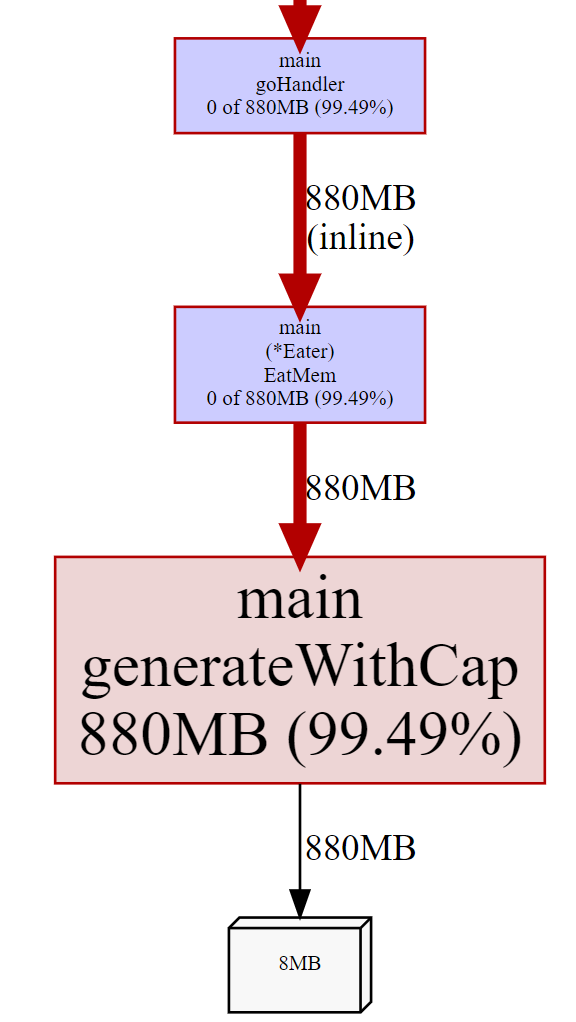
goroutine 使用: